WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?
Contents
- Definition of artificial intelligence
- The history of artificial intelligence
- What are the types of artificial intelligence?
- What is Artificial Intelligence used for?
- What are the popular Artificial Intelligences?
DEFINITION OF AI
Based on the imitation of human intelligence, artificial intelligence (AI) is a process of creating and applying algorithms that executes in a dynamic computing environment. Its objective is to allow computers to act, which means to make gestures and to think like humans.
To achieve this, components are necessary, at least 3:·
- Computer programs or applications·
- A gigantic database with sophisticated management systems.·
- Advanced AI algorithm programming.
To emulate human behavior as closely as possible, AI requires a considerable amount of data, high processing capacity and speed.
WHAT IS THE GENESIS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE?
Since the first century BCE, humans have always had a penchant for creating machines capable of imitating human reasoning or replacing it in certain areas. However, the term “artificial intelligence” is more recent, in 1955 by John McCarthy. In 1956, John McCarthy and his immediate collaborators organized a conference called the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, which gave rise to machine learning , deep learning , predictive analytics, and, more recently, prescriptive analytics. A new field of study has also emerged: data science.
It can also be traced back to the beginning of 1943 , with the publication of the article “A Logical Calculus of Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. » by Warren McCullough and Walter Pitts . In it, scientists present the first mathematical model for creating a neural network .
In 1950, Snarc , the first neural network computer , was created by two Harvard students: Marvin Minsky and Dean Edmonds. The same year, Alan Turing published the Turing Test which is still used to evaluate AI. From this test flow the foundations of artificial intelligence, its vision and its objectives: to replicate or simulate human intelligence in machines .
But it was not until 1956 that the term artificial intelligence was mentioned for the first time, during the “Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence” conference. » by John McCarthy. At this event, researchers present the goals and vision of AI. Many consider this conference to be the true birth of artificial intelligence as it is known.
Several years pass and work on artificial intelligence continues. In 1959, Arthur Samuel coined the term Machine Learning while working at IBM. In 1989, Frenchman Yann Lecun developed the first neural network capable of recognizing hand-written numbers; this invention was at the origin of the development of deep learning .
And it was ten years later, in 1997, that a major event marked the history of AI. IBM's Deep Blue system triumphs over world chess champion Gary Kasparov. For the first time, the machine has defeated Man .
WHY IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IMPORTANT?
Nowadays, there is a symbiosis between human beings and machines in the faster management of data that is not humanly possible to absorb and interpret to make complex decisions. Artificial intelligence is the basis of all computer learning and represents the future of complex decision-making processes. For example, most humans can learn not to lose in a simple game of tic-tac-toe, when there are 255,168 possible actions, of which 46,080 lead to a draw. On the other hand, checkers champions are rarer, given that there are more than 500 x 10 18 (500 trillion) possible moves. Computers are able to calculate these combinations and the best possible permutations very efficiently, in order to make the right decision. AI (with its logical evolution, machine learning ) and deep learning represent the future of decision-making.
AREA OF INTERVENTION OF AI
AI is present in our daily lives. For example, it is used by the fraud detection services of financial institutions, to predict purchasing intentions and in interactions with online customer services. Here are some examples :
· Fraud detection. In the finance industry, artificial intelligence is used in two ways. Apps that score credit applications use AI to assess consumers' creditworthiness. More advanced AI engines are responsible for monitoring and detecting fraudulent credit card payments in real time.·
Virtual Customer Service (VCS). Call centers use SCV to predict and respond to customer requests without human intervention. Voice recognition and a human dialogue simulator provide the first point of interaction with customer service. More complex requests require human intervention.·
When an Internet user opens a dialog window on a web page ( chatbot ), their interlocutor is often a computer running a form of specialized AI. If the chatbot cannot interpret the question or resolve the problem, a human agent takes over. These interpretation failures are sent to the machine learning system to improve future interactions of the AI application.
HOW IS AI LEARNING?·
Machine learning involves allowing the AI model to learn how to perform a task instead of specifying exactly how it should accomplish it 11 . The model contains parameters whose values are adjusted throughout training. The gradient backpropagation method is able to detect, for each parameter, to what extent it contributed to a correct response or an error of the model, and can adjust it accordingly. Machine learning requires a way to evaluate the quality of the answers provided by the model 12 .
THE MAIN LEARNING METHODS ARE:
An annotated dataset is used to train the algorithm. It contains input data provided to the model and the corresponding expected responses, which the model is trained to produce. It is sometimes difficult to obtain enough annotated data with the expected answers.
A dataset is provided to the model, but is not annotated with the expected responses. The goal can for example be to group similar data together ( clustering ).
A supervised learning problem is automatically generated from an unannotated dataset. This often works by hiding part of the information (words of a text, pieces of images, etc.) in order to train the model to predict it.
The agent is immersed in an environment where what he does is evaluated. For example, an agent can learn to play chess by playing against itself, and the result (victory or defeat) allows each iteration to evaluate whether it played well. In this case there is no need for a dataset.
Neural networks
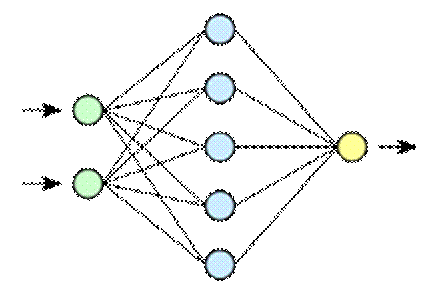
.Artificial neural networks are inspired by the functioning of the human brain : neurons are generally connected to other neurons at input and output. Input neurons, when activated, act as if participating in a weighted vote to determine whether an intermediate neuron should be activated and thus transmit a signal to the output neurons. In practice, for the artificial equivalent, the “input neurons” are just numbers and the weights of this “weighted vote” are parameters adjusted during training.
Aside from the activation function , artificial neural networks in practice only perform matrix additions and multiplications , so they can be accelerated by the use of graphics processors . In theory, a neural network can learn any function .
For simple feedforward neural networks , the signal only passes in one direction. With recurrent neural networks , the output signal of each neuron is fed back into that neuron's input, enabling a short-term memory mechanism. Convolutional neural networks , which are particularly used in image processing , introduce a notion of locality. Their first layers identify relatively basic and local patterns like contours, while the last layers deal with more complex and global patterns.
Deep learning
Deep learning uses multiple layers of neurons between inputs and outputs, hence the term “ deep ” 20 . The use of graphics processors to speed up calculations and the increase in available data has contributed to the rise in popularity of deep learning. It is used in particular in computer vision , automatic speech recognition and natural language processing (which includes large language models ).
Major language models
Large language models are language models with a large number of parameters, typically billions. They are very often based on architecture Generative Pretrained Transformers ( GPT ) are a particularly popular type of large language model. Their “pre-training” consists of predicting, given a part of a text, the next token (a token being a sequence of characters, typically a word, part of a word, or punctuation). This training in predicting what will come next, repeated for a large number of texts, allows these models to accumulate knowledge about the world. They can then generate text similar to that used for pre-training, by predicting the following tokens one by one . Typically, another training phase is then carried out to make the model more truthful, useful and harmless. This training phase (often using a technique called RLHF) makes it possible to reduce a phenomenon called “ hallucination ”, where the model generates information that appears plausible but is false.
Before being supplied to the model, the text is broken into tokens . These are converted into vectors which encode their meaning as well as their position in the text. Inside these models is an alternation of neural networks and attention layers. Layers of attention combine concepts together, allowing context to be taken into account and complex relationships to be captured.
These models are often integrated into chatbots , where the generated text is formatted to respond to the user. For example, the ChatGPT conversational agent uses the GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models 25 . In 2023, consumer models will appear that can simultaneously process different types of data such as text, sound, images and videos, such as Google Gemini .
Research and optimization
Some problems require searching intelligently among many possible solutions.
Local search
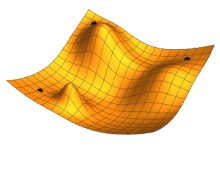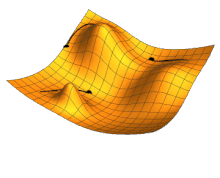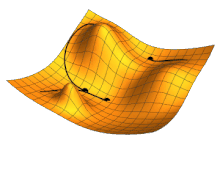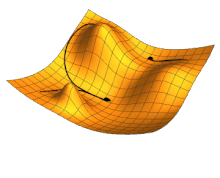
Illustration of gradient descent for three different starting points, varying two parameters so as to minimize the cost function represented by the height.
Local search , or optimization search, relies on mathematical optimization to find a numerical solution to a problem, gradually improving the chosen solution.
In particular, in machine learning, gradient descent makes it possible to find a locally optimal solution , given a cost function to be minimized by varying the model parameters. It consists, at each step, of modifying the parameters to be optimized in the direction which best reduces the cost function. The solution obtained is locally optimal, but there may be better solutions globally, which could have been obtained with different initial parameter values. Modern AI models can have billions of parameters to optimize, and often use more complex and efficient variations of gradient descent.
Evolutionary algorithms ( inspired by the theory of evolution ) use a form of optimization search. At each step, operations such as "mutation" or "crossover" are performed randomly to obtain different variants, and the best-matched variants are selected for the next step.
State space search
State space search aims to find a state accomplishing the objective through a tree of possible states 28 . For example, adversarial search is used for programs playing games such as chess or Go . It consists of going through the tree of possible moves by the player and his opponent, looking for a winning move. The simple exhaustive search is rarely sufficient in practice given the number of possible states. Heuristics are used to prioritize the most promising paths .
Logic
Formal logic is used for reasoning and knowledge representation . It comes in two main forms, propositional logic and predicative logic. Propositional logic operates on statements that are true or false, and uses connective logic with operators such as “and,” “or,” “not,” and “implies.” Predicative logic extends propositional logic and can also operate on objects, predicates or relations. She can use quantifiers as in “ Every X is a Y” or “ Some X are Y.”
Logical inference (or deduction ) is the process of providing a new statement (the conclusion) from other statements known to be true (the premises ). An inference rule describes the valid steps of a proof ; the most general is the resolution rule . Inference can be reduced to the search for a path leading from premises to conclusions, where each step is an application of a rule of inference 31 . But except for short proofs in narrow areas, exhaustive research takes too long.
Fuzzy logic assigns truth values between 0 and 1, making it possible to handle vague statements, such as “it’s hot.” Non-monotonic logic allows certain conclusions to be overturned. Various other forms of logic are developed to describe many complex areas.
Probabilistic methods and uncertainty management
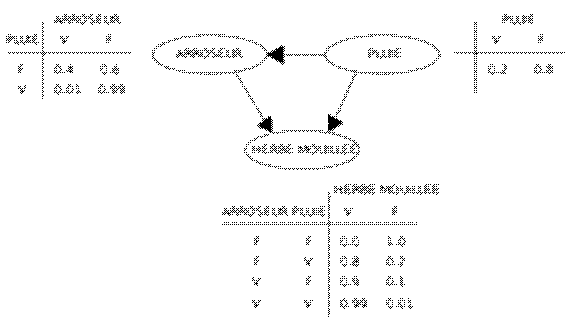
An example of a Bayesian network , and associated conditional probability tables.
Many problems in AI (reasoning, planning, learning, perception, robotics, etc.) require being able to operate from incomplete or uncertain information.
Some techniques rely on Bayesian inference , which provides a formula for updating subjective probabilities given new information. This is particularly the case for Bayesian networks . Bayesian inference often needs to be approximated in order to be calculated.
Monte Carlo methods are a set of techniques for solving complex problems by randomly performing numerous simulations in order to approximate the solution.
Neural networks can also be optimized to provide probabilistic estimates.
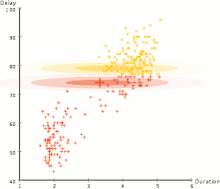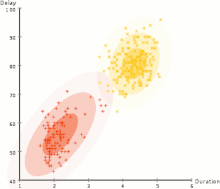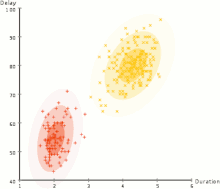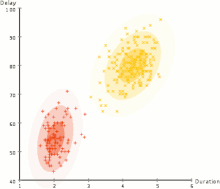
Separation of data into two groups ( partitioning ) by an expectation maximization algorithm .
Precise mathematical tools have been developed to analyze how agents can make choices and plans using decision theory , expectation maximization , and information value theory. These techniques include models such as Markovian decision processes , game theory , and incentive mechanisms .
Classifiers and statistical methods
Many AI models aim to assign a category ( classification ), a value (regression) or an action to provided data. Classification methods include decision trees , k-nearest neighbors , support vector machine, or naive Bayesian classification . Neural networks can also do classification.
History
Main article: History of artificial intelligence
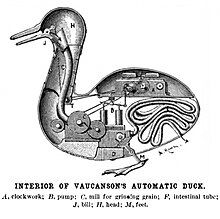
.Vaucanson 's artificial duck ( 1738).As a precursor to artificial intelligence, various automata have been created throughout history, including Vaucanson's duck or the Al - Jazari automata . Some automatons date back to Antiquity and were used for religious ceremonies. Myths and rumors also report the creation of intelligent beings, for example golems .
Philosophers and mathematicians like Raymond Lulle , Leibniz or George Boole sought to formalize reasoning and the generation of ideas 41 .
In the 20TH century , Alan Turing notably invented a model of calculation subsequently called Turing machine , explored the notion of computability and intelligence of machines, and proposed the "imitation game" ( Turing test ) to evaluate the intelligence of future machines 41 .
The term “artificial intelligence” was put forward by John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, where artificial intelligence was established as a discipline in its own right 42 , 43 . In the years since, researchers have proposed various proofs of concept , in specific situations, of what machines can theoretically do. For example, the ELIZA program could pose as a psychotherapist, and the Logic Theorist could demonstrate theorems 44 .The end of the century was marked by periods of enthusiasm, and two periods of disillusionment and freezing of funding called "AI winters" 45 , the first from 1974 to 1980 and the second from 1987 to 1993. The systems Experts were particularly popular in the 1980s, despite their fragility and the difficulty in manually implementing the correct inference rules 44 . Machine learning techniques have been developed ( neural networks , gradient backpropagation , genetic algorithms ) as well as the connectionist approach 44 . But low computing power and lack of training data limited their effectiveness. Certain areas were gradually no longer considered part of artificial intelligence, as an effective solution was found 46 ; a phenomenon sometimes called the “ AI effect .”
In the 2000s, Web 2.0 , big data and new infrastructures and computing capacities enabled the exploration of unprecedented masses of data. In 2005, the Blue Brain project began, aiming to simulate the mammalian brain 47 . In 2012, with the Alexnet convolutional neural network , the use of graphics processors to train neural networks began , thus increasing the computing capacities dedicated to learning 48 . Organizations aiming to create artificial general intelligence have emerged, such as DeepMind in 2010 49 and OpenAI in 2015 50 .
In 2017, researchers at Google proposed the transformer architecture , which served as the basis for large language models. In 2018, Yann Le Cun , Yoshua Bengio and Geoffrey Hinton won the Turing Prize for their work on deep learning 51 , 52 .
In 2022, programs generating images from textual descriptions, such as Midjourney or DALL-E 2 , have become popular 53 , and the conversational agent ChatGPT has shown unprecedented growth, gaining a million users in just five days 54 and one hundred million users in two months 55 , which has accentuated a phenomenon of “race” for AI 56 . By 2023, rapid advances in AI have raised concerns about the potential risk of human extinction . Models that simultaneously treat several modalities (text, images, sound) have emerged (including Google Gemini ) 58 .
General artificial intelligence [ edit | edit code ]
Main article: general artificial intelligence
.Artificial general intelligence (AGI) includes any computer system capable of performing or learning virtually any cognitive task unique to humans or other animals . It can alternatively be defined as a computer system outperforming humans in most tasks of economic interest 60 .
Artificial general intelligence has long been considered a purely speculative subject . Some research has previously described GPT-4 as having “sparks” of artificial general intelligence 62 , 63 . Artificial intelligence experts display wide disagreement and uncertainty about the potential date for the design of the first artificial general intelligences (sometimes called "human-level artificial intelligences"), their impact on society, and their potential to trigger a "human-level explosion" . 'intelligence ' 64 .
A 2022 poll suggests that 90% of AI experts believe AGI has more than a 50/50 chance of being realized within 100 years, with a median date of 2061 65 .
An artificial superintelligence is a hypothetical type of artificial general intelligence whose intellectual abilities would far exceed those of the most brilliant humans 66 . The philosopher Nick Bostrom notes that machines have certain advantages over human brains, particularly with regard to memory, speed (the frequency of processors being of the order of ten million times higher than that of biological neurons ) and the ability to share knowledge 67 .
Turing Test [ edit | edit code ]
In the Turing Test , a machine and a human respond verbatim to a human interrogator's questions. The interrogator does not see them but must determine from the textual responses which of the two is the machine. To pass the test, the machine must manage to deceive the interrogator a good part of the time. This test was designed by Alan Turing in 1950 in the article “ Computing Machinery and Intelligence ”. Originally called the "imitation game", its purpose was to provide a real-world experiment to determine whether machines can think

What are the types of artificial intelligence?
Thanks to the development of artificial intelligence and discovered technologies such as deep learning or machine learning , researchers agree to discern 3 types of artificial intelligence:
General artificial intelligence
General or deep AI is artificial intelligence capable of carrying out any cognitive task as a human or animal would do. Still considered hypothetical, some scientists question GPT-4 and the likelihood that it is an early form of general AI. To move in this direction, a large majority of AI researchers believe that humanity has the technology necessary to create general AI, in particular thanks to neural networks.
Strong artificial intelligence
We speak of strong AI or superintelligence when a model refers to philosophical knowledge and shows signs of its own consciousness . Close to a science fiction scenario, AI researchers nevertheless believe that strong AI is impossible to create currently. For them, the notion of consciousness and feelings cannot see the light of day in mathematical systems that manipulate and respond with symbols and calculations.
Weak artificial intelligence
The final distinction of artificial intelligence is weak or narrow AI . This AI is a system capable of carrying out a single task almost perfectly , without the need for human supervision. It is the most used model and created to accelerate various processes in different business sectors.
What is Artificial Intelligence used for?
Artificial intelligence has helped transform many sectors of activity , including medicine, science, finance, automobiles and many others.
In medicine , AI is used to diagnose and predict diseases, enabling early detection and rapid intervention. It is also applied in pharmaceutical research to accelerate drug discovery and improve treatments.
In scientific research , AI analyzes large amounts of data and makes discoveries in fields such as astrophysics, genomics, biology and chemistry. It accelerates scientific progress and opens up new research perspectives.
With the arrival of GPT-3.5 in November 2022, a powerful LLM , the potential of artificial intelligence has increased tenfold. From now on, we also use AI in creative fields such as the generation of texts, images and even in audiovisual, thanks to applications like VALL-E, Midjouney or even GEN-2.
Faced with the massive changes brought about by artificial intelligence, many people are also starting to question the dangers it could pose. Considered as dangerous as the nuclear bomb by business leaders, such as Sam Altman CEO of Open AI, or researchers, the latter believe that AI could become a threat to humanity .
Due to its ability to learn and evolve, AI could one day surpass humans in certain areas, and thus replace them. In any case, this is what the Goldman Sachs study suggests , affirming that, within a few years, more than 300 million jobs will disappear . At the same time, people are wondering about their privacy and personal data. Needing data to improve, will AI have access to everyone's personal data under the pretext of major technological and economic development? Concerned about this disaster scenario, Europe and other companies, like Google, are implementing regulations in their systems or through laws like the AI Act
But AI is not the only potential danger, it also depends on how it is used. Even seemingly harmless AI could be misused in a malicious way . We can already see this with the rise of “ DeepFakes ”: fake videos created using Deep Learning to depict a person in a compromising situation.
Artificial intelligence will continue to develop rapidly over the coming years. It is now up to humanity to regulate it to develop healthy and ethical AI .
What are some known examples of artificial intelligence?Artificial intelligence is only growing day by day, to the point where applications can now simplify or even automate everyday tasks. Here are 10 apps, powered by AI, that speed up everyday life.
- ChatGPT : we no longer need to introduce it, OpenAI 's famous text generator is the AI tool par excellence. Able to respond to all kinds of requests, this model has become the personal assistant of millions of people.
- DALL-E2 : This model is the most famous image by text generator today. Designed by OpenAI , its name is a portmanteau between Wall-E and the painter Salvador Dali.
- GEN-2 : this AI tool developed by Runway allows you to transform videos or create them from images or texts. With 5 transformation modes, Gen-2 is a complete video creation tool .
- TextCortex : compatible with around thirty sites (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc.) this plugin uses machine learning to translate more than 25 languages in a few seconds .
- GitHub Copilot : This artificial intelligence-based integrated development environment extension is developed by GitHub and OpenAI . It helps developers by automatically completing their code .
- Adobe Firefly : this AI engine from Abode only uses royalty-free photos to generate its new creations. Adobe prides itself on its AI being the first ethical image generation AI
- Bard AI : bard is Google's intelligent chatbot . Not yet available in Europe , Google wants to implement an ethical AI policy that does not misinform its users.
- Jasper : the software is aimed at all written content creators. It allows you to write articles 5 times faster with different tones and angles
- Spotify DJ : even the music platform Spotify has tried its hand at artificial intelligence. Thanks to DJ, the application can offer playlists entirely based on the user's tastes and evolve according to their choices
- Gamma.app : this very impressive artificial intelligence tool allows you to create slideshow-style visual presentations in just a few clicks.